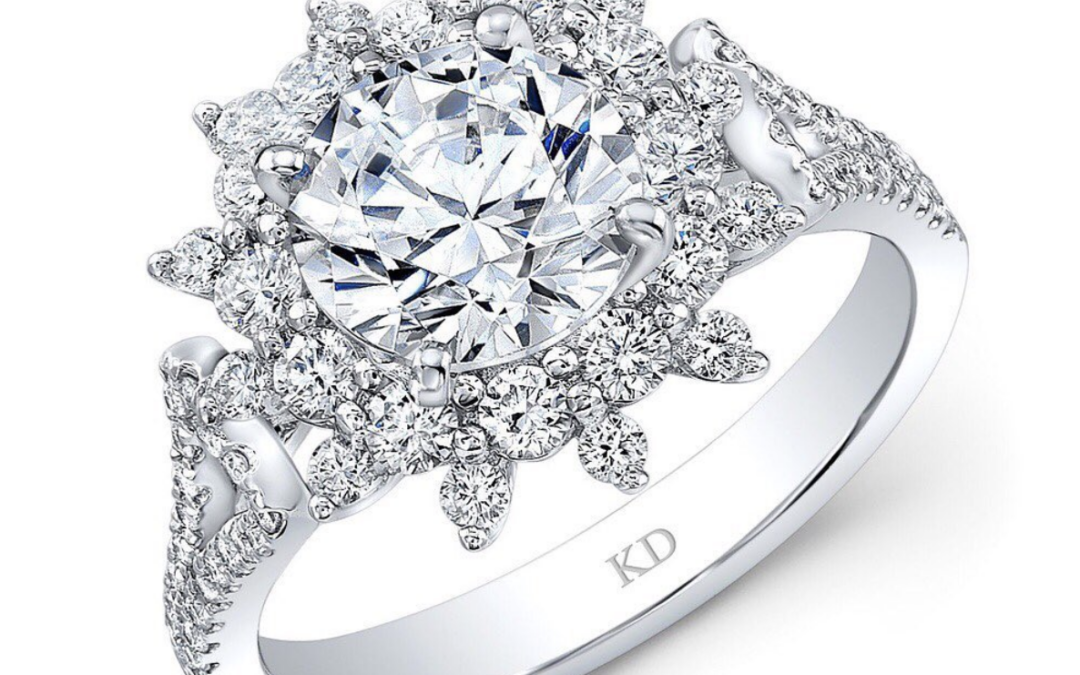
Buying diamonds can be a scary and overwhelming process, and sometimes you just don’t know what you don’t know! Take a look at our comprehensive diamond buying guide to prepare beforehand, and make sure you are ready and confident to find the perfect diamond for yourself or your loved one!
The Basics:
How to Buy Diamonds
The best explanation is that asking for the price of a diamond is like asking for the price of a house. A real estate agent can’t give you a price without knowing the size, condition, location, and quality. This process is the same as buying a diamond. A diamond’s beauty, rarity, and price depend on the 4Cs – cut, clarity, carat, and color.
Once you have established the 4C characteristics that are most important to you, our jewelers can then begin to show you various options within your price and preference range.
What to Spend on Diamonds
Diamonds can be found in a range of prices and we’ll help you find the ones within the Diamond Quality Pyramid that suit your taste and price point. If you’re about to buy a diamond engagement ring, you may want to consider spending the commonly accepted guideline of two months salary – but it’s actually fully up to you to decide on a price!
The 4 C’s of Diamond Buying
Before investing in a diamond, it’s important to learn how to be sure you are getting what you pay for. Understanding how a diamond’s value is determined will help you make decisions based on price and quality. You may prefer a larger stone, for example, with somewhat less clarity or slight flaws instead of a flawless, smaller diamond.
1) Cut
A diamond’s cut—its shape and facets—is what makes it sparkle. The more faceted the cut, the greater the sparkle. Popular cuts include the round (57 facets), rectangular emerald (44 facets), the square princess (50 or 58 facets), the oval (56 facets), the slender marquise (58 facets), and the hybrid pear (58 facets).
2) Clarity
Clarity measures the purity of the diamond and the presence of small flaws or faults. The clearer (or more flaw-free) the diamond, the more brilliant and valuable it is. Internal flaws are inclusions, while external ones are blemishes.
Jewelers and gemologists use the scale FL (flawless) VVS (very, very slightly included), SI (slightly included), I (included), with number grades for each category as well.
3) Carat
A diamond’s weight is measured in carats. A carat is 200 milligrams, and each carat can be subdivided into 100 points. Diamonds that are more than one carat are expressed in decimals, like a 1.15-carat diamond. The price per carat increases according to a diamond’s size since larger stones are rarer.
4) Color
Diamonds come in many colors and are categorized as either white—essentially colorless—or fancy. These variations make a major difference in diamond quality and price – though this can change with fashion and popularity. Depending on the fashion, hue, and intensity, a stone’s color can either diminish or enhance its value!
The color scale for diamonds consists of D to Z. All D-Z diamonds are considered white, even though they contain varying degrees of yellow and brown.
Perfectly colorless diamonds at the D end of the spectrum are considered the highest quality and the most expensive. Colorless or clear white diamonds are more desirable, as they allow the most refraction of light or ‘sparkle’.
Buying Diamonds With Confidence At Village Jewelers of Frisco
A good jeweler is the first step to a smart diamond purchase. Your jeweler should be knowledgeable about diamonds and help you feel comfortable making this important purchase! Contact Village Jewelers or come visit us today to find your perfect diamond.