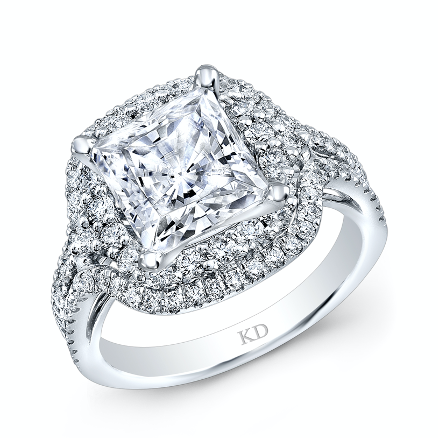
When selecting the perfect diamond, whether for an engagement ring, anniversary gift, or personal indulgence, understanding the 4Cs—Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat—is essential. These four characteristics determine a diamond’s quality, appearance, and value. At Village Jewelers, we strive to empower our clients with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
Cut: The Sparkle Factor
The cut of a diamond refers to how well it has been shaped and faceted, impacting its brilliance and sparkle. A well-cut diamond reflects light internally and disperses it through the top, creating that signature sparkle. Cuts are graded from Excellent to Poor, with Excellent cuts maximizing light return.
A poorly cut diamond, regardless of its color or clarity, can appear dull. Therefore, cut is often considered the most crucial of the 4Cs.
Color: The Hue Spectrum
Diamonds are graded on a color scale established by the Gemological Institute of America (GIA), ranging from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown). Colorless diamonds (D-F) are rare and highly valued, while near-colorless diamonds (G-J) offer excellent value with minimal visible color differences.
The choice of metal can influence how a diamond’s color is perceived. For instance, warmer colored diamonds (K-Z) may appear more vibrant when set in yellow gold, while colorless diamonds (D-J) look stunning in white gold or platinum.
Clarity: The Purity Indicator
Clarity assesses the presence of inclusions (internal flaws) and blemishes (external imperfections) in a diamond. The GIA clarity scale ranges from Flawless (F) to Included (I1-I3).
- Flawless (F): No inclusions or blemishes visible under 10x magnification.
- Internally Flawless (IF): No inclusions, only minor blemishes visible under 10x magnification.
- Very Very Slightly Included (VVS1 and VVS2): Minute inclusions difficult to detect under 10x magnification.
- Very Slightly Included (VS1 and VS2): Minor inclusions observed with effort under 10x magnification.
- Slightly Included (SI1 and SI2): Noticeable inclusions under 10x magnification.
- Included (I1, I2, and I3): Obvious inclusions under 10x magnification, which may affect transparency and brilliance.
While flawless diamonds are rare and expensive, many inclusions are microscopic and do not affect a diamond’s beauty. Some inclusions can be hidden by settings, making diamonds with lower clarity grades more affordable without compromising appearance.
Carat: The Weight Measure
Carat measures a diamond’s weight, not its size. One carat equals 200 milligrams. Diamonds are also measured in points; 100 points equal one carat. For example, a 0.75-carat diamond is 75 points.
Larger diamonds are rarer and thus more valuable. However, two diamonds of equal carat weight can have different values based on their cut, color, and clarity. Additionally, a well-cut diamond can appear larger than its carat weight suggests, offering better value.
Making an Informed Choice
Understanding the 4Cs helps you prioritize what’s most important to you, whether it’s size, sparkle, purity, or colorlessness. At Village Jewelers, our experts are here to guide you through each characteristic, ensuring you find a diamond that fits your preferences and budget.
For more detailed information, visit our Diamond Buying Guide.